Network
The Network page allows you to view and change network configuration information for the DXi9000 Series. The DXi9000 Series uses this information to connect to the network.
Network configuration information is entered during initial setup DXi9000 Series. You should consult your network administrator before making any changes to the network settings.
Note: If you have more than one IP address configured on your DXi9000 network page, Quantum recommends that you implement static routes to the replication partner (both from source to target and from target to source).
Caution: Changing the network configuration requires a system reboot to allow all system services to function correctly. Changing the network configuration requires a system reboot immediately after the changes are applied.
Additional Information
- Before configuring the network, work with your network administrator to determine the network settings that will be required to properly integrate the DXi9000 Series with your company’s network.
- An existing valid network configuration must already have been entered during system setup when running the Getting Started Wizard.
- Rebooting the system can take several minutes. After the new network configuration is saved, close your Web browser and wait 15 minutes before logging in again. If you change the IP address that you use to log in to the system, you will temporarily lose your connection to the remote management console. Because of this, you might not see the confirmation page informing you that the new settings have been saved.
To access the Network page, select the Configuration menu and then click the System > Network tab.
Using the Network > General and Network > IP Address Config pages, each physical Ethernet port in the DXi can be configured as a separate device. In addition, you can create bonded devices (logical ports) consisting of two or more physical virtual ports of the same link speed (1GbE or 10GbE). For each port or device, you can specify the MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) frame size.
After you define devices, specifying single port or bonded, you can create up to ten network interfaces for each device. Each interface has its own IP address information. In addition, you can configure the following options for each interface:
- Assign the interface to a VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network).
- Indicate whether the interface IP address will be used to externally identify the system (external host IP address).
- Specify the types of traffic allowed on the interface (management, replication, or data).
- Specify the NAT address where the interface is mapped if it is used for replication through a NAT firewall.
- Add routing information for an interface to enable connectivity with devices on different subnets.
Note: You can choose to allow any traffic type (management, replication, or data) on an interface. In this case, the routing of different traffic types, as well as firewall capability, must be controlled using the network infrastructure (routers and switches) where the system is connected.
Note: Before configuring the network, work with your network administrator to determine the network settings that will be required to properly integrate the DXi9000 Series with your company’s network.
Configuring the network includes the following major steps:
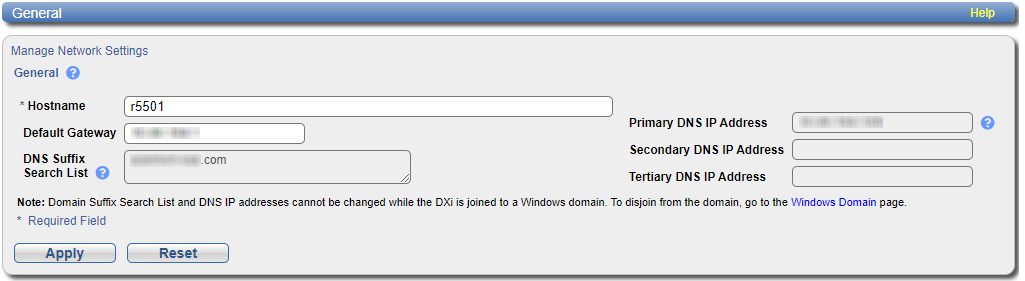
From the Configuration > System page, select the Network > General tab, and then enter the following network information as provided by your network administrator:
Additional Information
- When entering IP addresses, never use an address that is in a reserved IP address range. To see a list of reserved IP address ranges, click the quick tip icon [
 ] located below Manage Network Settings, under General.
] located below Manage Network Settings, under General. - The DNS Suffix Search List and DNS IP Addresses cannot be modified if the DXi9000 Series is currently joined to a Windows domain. To disjoin a Windows domain, see Disjoining a Workgroup or Domain.
| Hostname |
The hostname of the DXi9000 Series. The Hostname cannot be blank and must contain only letters Note: Using uppercase letters in the hostname is acceptable but will not be preserved after entry. For that reason, Quantum recommends using lowercase letters in the Hostname or IP Address box. |
| Default Gateway |
The default gateway IP address. Specifying a default gateway is optional if all access is local to a particular subnet. For example, if the DXi9000 Series and all of its clients are on the same subnet, you do not need to specify a default gateway. Caution: Specifying a default gateway is required to enable connectivity with all subnets other than those that the DXi9000 Series is directly connected to. For example, if the DXi9000 Series and its clients are on different subnets, or you are using an external NTP server, you must specify a default gateway. |
| DNS Suffix Search List |
(Optional) The domain list to search when resolving domain names. The list may be either a single domain name or a comma-separated list of up to 6 domain names. The first domain name listed is used as the local domain. Domain names must contain only letters [ A–Z, a–z ], numbers [ 0–9 ], dots [ . ], and hyphens [ - ]. |
| Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary DNS IP Address |
(Optional) The IP addresses of up to three DNS servers used to resolve domain names and translate them into IP addresses. Note: You must specify a DNS IP address if you plan to use hostname format when configuring an NTP time server, outgoing email server, replication sources and targets, and other information. |
From the System tab, select Network >General, and then under Bonding Details, use this section to aggregate multiple ports into a single group, with total bandwidth combined into the single (bonded) connection:
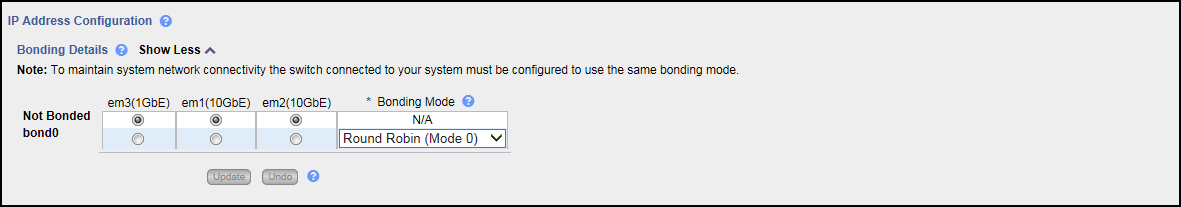
- If necessary, click the Show More link to show the bonding details table.
-
For each available bonded device, select two or more Ethernet ports with the same link speed to assign to the bond. Or select Not Bonded to leave a port unassigned to any bond.
If no ports are assigned to a bond, the bond cannot be configured. That is, settings cannot be entered for the bond in the Interface Details or IP Address tables because no Ethernet ports are assigned to the device.
All ports assigned to the same device are bonded together into a single logical port. A bonded device can contain two or more ports.
All ports associated with a bond must have the same link speed (1GbE or 10GbE).
-
For each bonded device, specify the bonding mode:
Note: To maintain network connectivity, the switch connected to the DXi9000 Series must be configured to use the same bonding mode. The best time to change the bonding mode on the switch is during the next reboot of your system, after saving the new network settings. Changing the bonding mode on the switch before saving these settings and rebooting may result in the loss of network connectivity to the system.
Bonding Mode Description Round Robin (Mode 0) This option sends Ethernet frames using the bonded Ethernet ports with a valid MII link. Frames are sent in a round-robin fashion, starting with the first slave device and then the rest of the devices. This only applies to the traffic sent from the DXi9000 Series. The Ethernet switch needs to aggregate the ports, so the connected ports are treated as a logical port. The DXi frame reception is completely dependent on the transmission algorithm of the Ethernet switch. The bonding mechanism does not balance the frame reception.
WARNING: The use of Round Robin (Mode 0) may cause TCP packets to arrive out of order. This can cause timeouts in the transfers.
LACP (Mode 4) This option (Link Aggregation Control Protocol) is based on the 802.3ad IEEE standard for aggregating Ethernet ports. If the bonding algorithm is set to LACP, the Ethernet switch ports must be configured in a 802.3ad based Link Aggregation group (LAG) in LACP mode. The DXi frame reception and transmission is controlled by the LACP between the bonded ports and the Ethernet switch ports.
Active Backup (Mode 1) This option does not require switch configuration but may not provide the same level of load balancing and performance as other bonding modes. Only one port in the bond is active at a time. If the active port fails, another port becomes active to take its place. Because only the MAC address of the active port is visible to the Ethernet switch, the switch does not require additional configuration. -
Click Update to save the changes you made to the Bonding Details table. (Clicking Update does not yet apply the new network settings to the DXi9000 Series.)
Note: Click Undo to revert to all current Bonding Details changes to the last update.
-
To apply network settings to the bonded connection, refer to Configuring Interface IP Addresses below.
Note: DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) is not supported. You must provide a static IP address at the time of installation.
Under IP Address Configuration > Interface Details, configure jumbo Ethernet frame settings for each port or device:
- If necessary, click the Show link to show the interface details table.
-
For each device, select the MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) frame size in the Jumbo Frame MTU Size drop-down box.
1500 MTU (Default) The standard (STD) MTU frame size of 1,500 bytes is used. 9000 MTU The jumbo MTU frame size of 9,000 bytes is used. (For best performance, make sure the entire network path to the DXi is configured to use 9000 MTU.) - Click Update to save the changes you made to the Interface Details table. (Clicking Update does not yet apply the new network settings to the DXi9000 Series.)
- Click Undo to revert to all current Interface Details changes to the last update.
Under IP Address Configuration > IP Address Table, configure one or more network interfaces for each physical or virtual Ethernet port or bonded device:
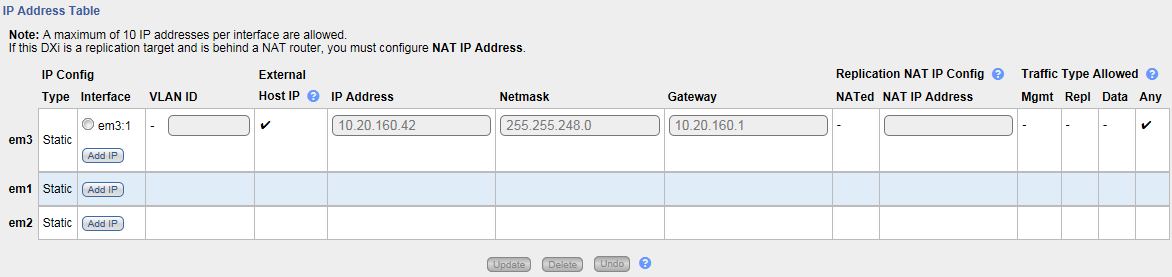
-
Click Add IP to add a network interface to a device.
Or select an interface to edit the IP address, netmask, gateway and traffic type. (To select an interface, click the radio button next to the interface index name, for example, bond0:2.)
Note: A maximum of 10 IP addresses are allowed per device. All IP addresses in the IP Address Table (added or modified) must be valid and unique, and must have a valid gateway and netmask.
-
In the VLAN ID column, select the check box to enable VLAN tagging for the interface. (Or clear the check box to disable VLAN tagging for the interface.)
VLAN tagging allows you to assign an interface to a virtual local area network (VLAN). With VLAN tagging, you can route different traffic types (management, data, and replication) over different VLANs, making sure traffic types do not mix.
If VLAN tagging is enabled, enter the VLAN Tag ID for the interface. (Valid values are 2 to 4094. You can assign only one tag ID to an interface.)
Additional Information
- The maximum allowed number of VLAN tag IDs is 64. If you attempt to add more than 64 VLAN tag IDs, an error displays.
- To maintain connectivity, the switch ports connected to the DXi must be configured to accept the correct VLAN tag ID.
Caution: If VLAN tagging is enabled for an interface, DXi Advanced Reporting is unable to collect and record statistics for traffic moving over the VLAN interface (for example, eth1.400). Statistics are still collected for the base device (for example, eth1.)
-
In the External Host IP column, select the check box to designate the interface as an external host IP. This associates the interface IP address with the host name of the DXi, and the DXi is externally identified by the host IP. The following restrictions apply:
- You can designate only one external host IP for the network configuration.
- You must specify a traffic type of Mgmt (management) or Any for the external host IP interface.
- You must specify a valid Default Gateway in the General section. In addition, the external host IP must be on the same subnet as the Default Gateway to ensure external communication.
-
Enter the following network information as provided by your network administrator (all fields are required):
IP Address The IP address of the interface. Netmask The network mask of the interface. Gateway A gateway in the network specified by IP address and netmask. (This is usually not the same as the default gateway. If the network has no gateway, the IP address is entered as the gateway.) -
If necessary, specify NAT (Network Address Translation) settings for the interface:
Note: If the DXi9000 Series is a replication target and is behind a NAT router, you must configure a NAT IP Address
NATed Select the check box if the IP address of the DXi is translated by a firewall to a NAT IP address when the DXi communicates to the outside world. NAT IP Address The IP address used to access the DXi from the public network. The router that connects the DXi to the Internet performs Network Address Translation that maps the IP address of the DXi to the NAT IP address, providing a valid replication interface for a source DXi. -
Select the check box for each type of network traffic allowed on the interface (segmentation):
At least one interface must allow management traffic.
Mgmt Select to allow management traffic. Repl Select to allow replication traffic. Data Select to allow data traffic. Any Select to allow all types of traffic. Additional Information
-
At least one interface must allow management traffic.
-
If a default gateway exists, the default gateway must be the gateway of an interface.
- If the DXi is configured for source or target replication, you should configure at least one interface to allow replication traffic (select Repl or Any) before applying changes to network settings.
- If you configure segmentation for non-bonded interfaces (Ethernet ports) that are on the same subnet, all traffic will use the lowest numbered Ethernet port first, no matter how segmentation is configured. To avoid this issue, create bonded interfaces, and then select the desired traffic type for each bonded interface.
-
- Click Update to save the changes you made to the IP Address table. (Clicking Update does not yet apply the new network settings to the DXi9000 Series.)
- Click Delete to remove IP address information for the selected interface. Or click Undo to revert all current IP Address Table changes to the last update.
Note: When you add a network interface, a default route (via the default gateway) is automatically created for the interface after network settings are applied and the DXi reboots. For example, if you add an interface with IP address 10.20.185.172, a route with the destination IP address 10.20.185.0 is automatically added. If you delete the default route, it is automatically added again the next time network settings are applied and the DXi reboots. For more information about interface routing, see Configuring Interface Routing.
Some network configurations require that you specify routing details for an interface. You need to specify routing details if the host or client the interface connects to is on a different subnet that is not reachable using the default gateway. You also need to specify routing details if you have configured multiple network segments (replication, data, or management) on the same subnet. For more information and examples, see Example 2: Segments and Target on the Same Subnet.
Under IP Address Configuration > Routing Details, enter routing information for one or more interfaces.
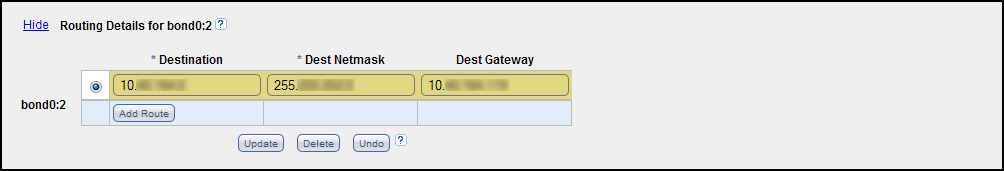
-
In the IP Address Table (above routing details), select an interface to add or modify routing data. (To select an interface, click the radio button next to the interface index name, for example, bond0:2.)
After selecting an interface in the IP Address Table, the Routing Details table below expands to display available routes (if any).
Note: A maximum of 8 routes per interface are allowed.
- If necessary, click the Show link to show the routing details table.
-
Click Add Route to add a route to the selected interface.
Or select a route to edit its settings.
-
Enter the following network information as provided by your network administrator:
Destination The destination network for the route. Dest Netmask The network mask for the route. Dest Gateway The gateway IP address used for outgoing traffic sent from the interface to a host or client. (This is usually not the same as the default gateway.) Additional Information
- The destination gateway of each route must match the subnet of at least one configured IP address listed in the IP Address Table. If no match is found, an error displays stating that the route’s destination gateway is not reachable.
- In the example shown below, to reach a host on the 10.50.50.x subnet, you would enter 10.50.50.0 for destination network, 255.255.255.0 for the destination netmask, and 10.20.20.1 as the destination gateway.
- Click Update to save the changes you made to the Routing Details table. (Clicking Update does not yet apply the new network settings to the DXi9000 Series.)
- Click Delete to remove IP routing information for the selected interface. Or click Undo to revert all current Routing Details changes to the last update.
For network changes to take effect, you must apply the changes, finalize the confirmation, and reboot the system.
-
To apply all changed settings on the Network page to the DXi9000 Series, click Apply at the bottom of the page.
-
Click on Yes to apply the selected configuration and routing settings.
Note: The following network setting changes do not require a system reboot:
-
Hostname
-
DNS IP Address
-
Domain Search Prefix
-
MTU Size
-
Select one of the following options.
The Confirmation screen displays the network settings to be applied to the system.
The Confirmation dialog is displayed.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Yes |
Your updated network settings are now active. |
| No | The Network > IP Address Config page is displayed. Changes made to the settings remain but are not applied. |
For a network on the interface to communicate with a host located on a different subnet, you must specify routing information in the Routing Details section. Routing is used to direct outgoing traffic from a network interface on the DXi to an IP address in another subnet by means of a destination gateway. Responses from the destination are routed back to the DXi using the gateway specified for the interface in the IP Address Table section.
In addition, when configuring segmented network interfaces, if the source DXi replication, data, and management interfaces are on the same subnet, you must add a host route on the source DXi to make sure the replication interface is correctly selected when replicating data to the target DXi.
See the following examples for details:
In the example below, the DXi has two segmented interfaces, one for management traffic and one for data traffic:
- The management interface is assigned to the 10.30.24.x subnet in the IP Address Table section. This subnet connects to the corporate network by mean of the default gateway (10.30.24.1).
- The data interface is assigned to the 10.20.20.x subnet in the IP Address Table section. This subnet connects to a gateway at 10.20.20.1.
-
Using the data interface, the DXi needs to connect to a backup host that is on the 10.50.50.x subnet. Because this host is not on the same subnet as the data interface, the DXi cannot communicate with the host unless you specify routing information in the Routing Details section.
In this example, you would specify 10.50.50.0 for destination network, 255.255.255.0 for the destination netmask, and 10.20.20.1 as the destination gateway.
Note: The gateway specified in the IP Address Table section is for incoming traffic to the interface. The gateway specified in the Routing Details section is for outgoing traffic from the interface.
Note: Alternately, should the route to the different subnet fail to be taken into account due to noncompliance between the IP address class and the netmask, you can configure the route to the sole replication partner’s IP instead of its subnet by using:
In the example below, the DXi has two segmented interfaces, one for data and management traffic, and one for replication traffic:
- The source DXi management/data IP address, the source DXi replication IP address, and the target DXi IP address are all on the same subnet (192.168.10.x).
- To make sure the replication segment is used when communicating with the target DXi, you must add a host route in the Routing Details section on the source DXi.
In this example, you would specify the following routing details for the replication interface on the source DXi:
| Destination | Use the IP address of the target DXi (192.168.10.200). |
| Dest Netmask | Use 255.255.255.255. |
| Dest Gateway | Use the replication IP address of the source DXi (192.168.10.100). |

In the example below, the DXi has two segmented interfaces, one for data and management traffic, and one for replication traffic:
- The source DXi management/data IP address and the source DXi replication IP address are on the same subnet (192.168.10.x). The target DXi IP address is on a different subnet (192.168.20.x)
- To make sure the replication segment is used when communicating with the target DXi, you must add a network route in the Routing Details section on the source DXi.
In this example, you would specify the following routing details for the replication interface on the source DXi:
| Destination | Use the subnet of the target DXi (192.168.20.0). |
| Dest Netmask | Use 255.255.255.0. |
| Dest Gateway | Use the IP address of the gateway (192.168.10.1). |
- In addition, to enable communication with the target DXi by means of the gateway, you must add a second host route in the Routing Details section on the source DXi.
In this example, you would specify a second set of routing details for the replication interface on the source DXi:
| Destination | Use the IP address of the gateway (192.168.10.1). |
| Dest Netmask | Use 255.255.255.255. |
| Dest Gateway | Use the replication IP address of the source DXi (192.168.10.100). |

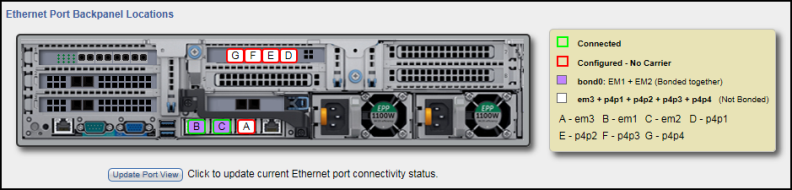
The Backpanel Locations section at the bottom of the Network page displays a graphical representation of the virtual Ethernet ports as they appear on the rear of the system.
The diagram indicates the current bonding configuration and connectivity status for all Ethernet ports.
- Ports that are bonded together in an interface are shaded the same color.
- A green border indicates a port is connected to a network.
- A red border indicates a port is configured but is not connected to a network.
- Click Update Port View to update the information on the diagram.
Allow the system to run a periodic check whether it has access to the Internet. To enable, select the Enable verification checkbox and click Apply.

From the Configuration > System page, select the Network > Firewall tab, and then use this page to show rules and ports where the system firewall is enabled.
Select the Enable Firewall check box to enable your system's firewall, after which you can click on:
-
Show rules - Lists the rules in place for each port where the system firewall is enabled.
-
Show ports - Shows each physical port configured with the system firewall enabled, in real time.
Note: The Enable Firewall check box must be enabled to activate the Show rules and Show ports buttons.
