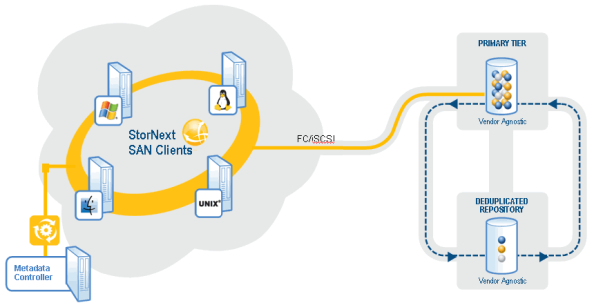
How Deduplication Works
When a file is initially created in a directory managed by StorNext deduplication, all of the application data is created in that file. Later, the file may be ingested by StorNext. During the ingest process the file will be split (logically) into segments called blobs, which is short for “binary large objects.”
Each blob is stored in the machine's blockpool, and has a unique blob tag associated with it. From the list of a file’s blob tags, StorNext can reconstitute the file with data from the blockpool.
If several files contain the same blob, only one copy is stored in the blockpool.
If StorNext file truncation is enabled for the deduplication policy, the original file can be "truncated." (This means that the space for the original file is released and can be re-used.) When part or all of the original file data is needed by an application, the data is retrieved from the blockpool. This concept of file truncation is similar to the file truncation available with StorNext Storage Manager.
The following graphic illustrates how deduplication works.
Figure 1: Deduplication